Quickly Learn Blockchain in this Crypto Crash Course!
People regularly sling terms like Blockchain, Crpyto, and Bitcoin without any explanation of what they mean. We are releasing various articles to get you up to speed with your cryptocurrency obsessed friends. Here is a brief introduction to the blockchain.

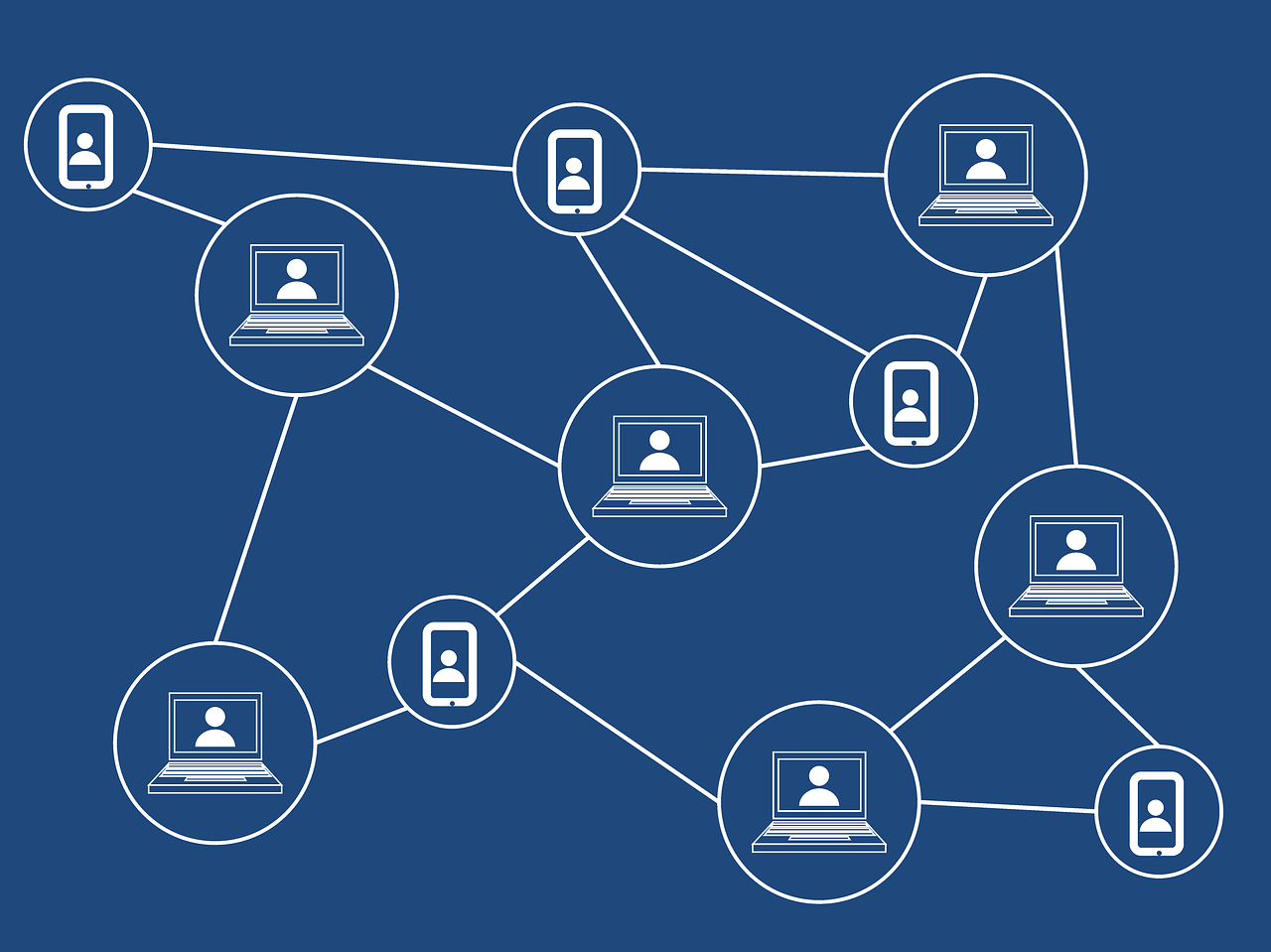
A Blockchain is a Distributed Ledger.
A ledger is a way of recording transactions between parties. Financial transactions get recorded with other data such as transaction times, parties involved, quantities and other such data. Traditionally, this information has existed in paper ledgers. These were ways for companies and individuals to record flows of value.
More recently, digital ledgers such as Microsoft Excel books keep track of transactions. These are all examples of centralized ledgers. Centralized ledgers mean that all of the sales are recorded and updated by a central party. A blockchain, on the other hand, is a distributed ledger. Unlike traditional paper ledgers of Excel workbooks, a distributed ledger records the transaction and shares an updated version of the ledger to everyone on the network. The ledger itself is immutable, meaning no one can reverse an operation that has already taken place.
A visual way of representing this is like an insect trapped in amber. The insect itself is perfectly preserved, and cannot be altered. However, the insect, which represents the transaction, is visible perfectly for anyone else on the network to see. As more and more transactions take place, the layers of clear amber increase over the insect, and it becomes more and more difficult to alter the trade that took place. Records of these transactions can be seen by everyone on the network, ensuring an accurate consensus by everyone involved.
Blockchain's Grand Entrance
The world’s very first blockchain was Bitcoin, created in 2009, which allowed anyone to interact with this brand new technology in a peer-to-peer way. The word block in blockchain refers to a block of transactions. These are transactions that are bundled together that require validation. Validating blocks means confirming that person X did indeed have enough funds to send to person Y and that the transaction records on the distributed ledger. Validating these blocks of trades are done by miners. Miners are parties who commit computing resources into confirming that a trade took place. Mining involves computers solving complex problems and reaching a solution which validates a transaction took place. The incentive for miners to authenticate transactions is that they receive rewards. In the case of Bitcoin, rewards are obtaining Bitcoins themselves.